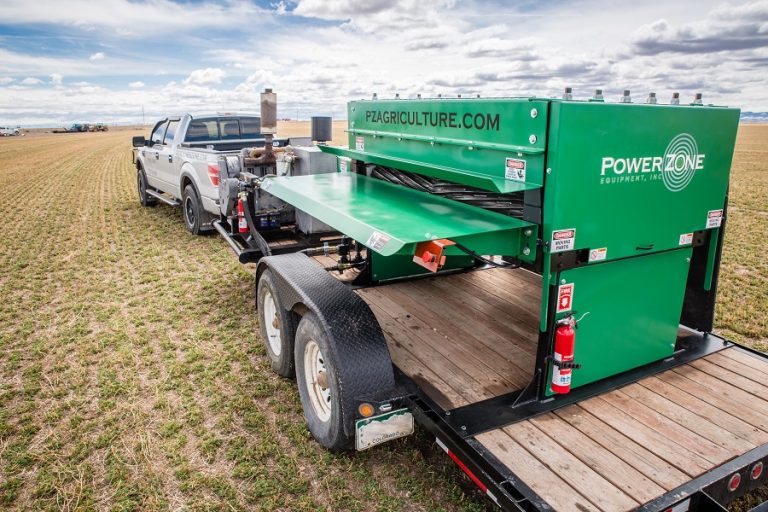
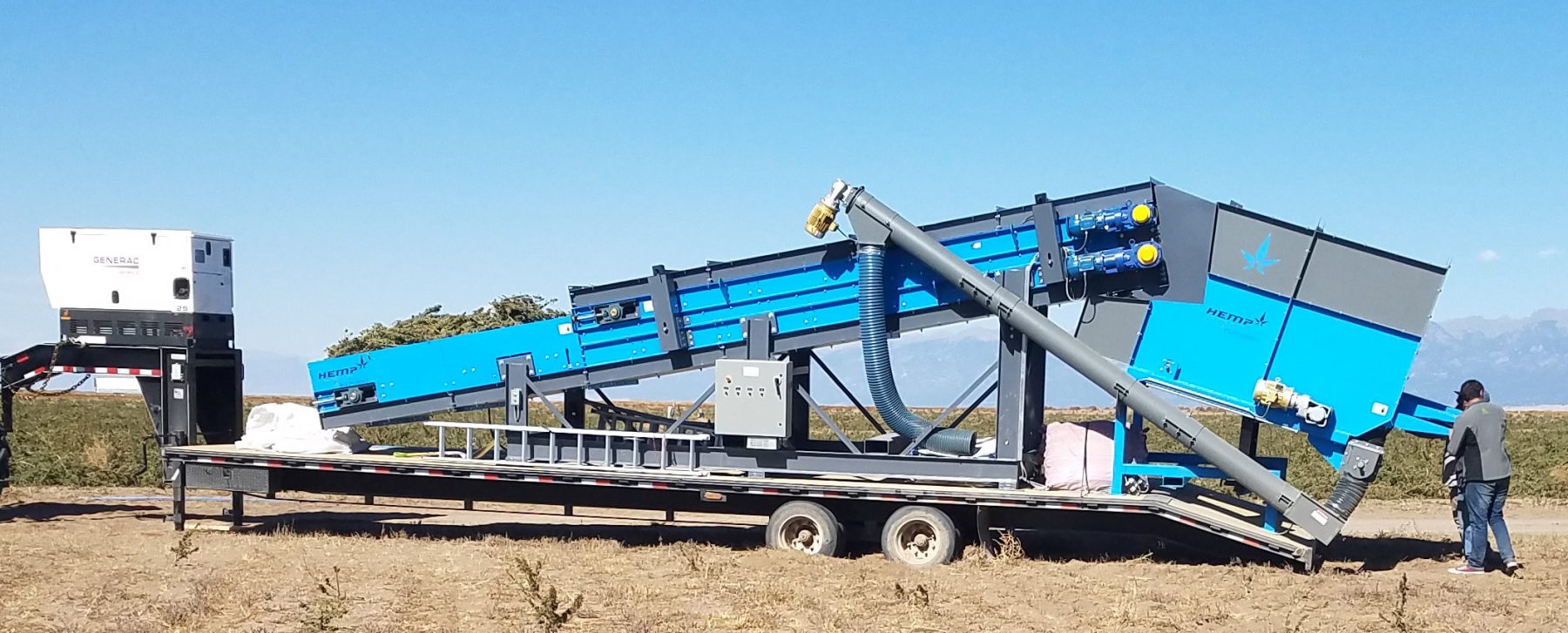
A mobile workplace for land cultivating purposes would be a self-contained unit that could be transported to different locations to perform various agricultural tasks. It would typically include the following features:
- Shelter: A weather-protected space for workers to operate machinery, store tools and equipment, and take breaks.
- Office Space: A dedicated area for planning, record-keeping, and communication.
- Storage: Secure compartments for storing seeds, fertilizers, crop yields, and other essential supplies.
- Power Generation: Solar panels or wind turbines to provide electricity for lighting, machinery, and other electrical needs.
- Water Storage and Purification System: Tanks for storing water for irrigation, sanitation, and consumption, along with a purification system to ensure water quality.
- Waste Management System: A responsible waste disposal system to minimize environmental impact and maintain a clean working environment.
- Mobile Machinery: Tractors, harvesters, and other agricultural equipment mounted on trailers or platforms for easy transport.
- Connectivity: Internet access to facilitate communication, access to information, and remote monitoring of operations.
- Living Quarters: If the mobile workplace is intended for extended stays in remote locations, it may include sleeping accommodations, basic cooking facilities, and sanitation facilities for workers.
The specific design and features of a mobile workplace for land cultivating purposes would vary depending on the type of crops being grown, the scale of operations, and the climate conditions of the working environment. However, the key principles of self-sufficiency, sustainability, and adaptability would remain central to its design.
Here are some additional considerations for setting up a mobile workplace for land cultivating purposes:
- Permits and Regulations: Obtain necessary permits and comply with local regulations regarding the use of mobile workplaces in agricultural settings.
- Logistics and Transportation: Develop a logistical plan for transporting the mobile workplace to different locations, ensuring efficient movement and minimal disruption to agricultural activities.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Implement a regular maintenance schedule for machinery, equipment, and the mobile workplace structure to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Emergency Preparedness: Develop emergency procedures and have necessary equipment in place to respond to potential hazards such as fires, weather events, or equipment malfunctions.
- Community Engagement: Engage with local communities to ensure that the presence of the mobile workplace is beneficial and does not negatively impact their livelihoods or environment.
By carefully planning, designing, and operating a mobile workplace for land cultivating purposes, agricultural activities can be conducted efficiently, sustainably, and with minimal environmental impact, contributing to a more productive and responsible approach to farming.